Setting up Cluster Orchestrator for AWS EKS clusters (Beta)
To enable Cluster Orchestrator for AWS EKS clusters associated with your account, follow these two simple steps:
Step 1: Enable feature flag
Currently, this early access feature is behind a feature flag . Contact Harness Support to enable the feature. After it is enabled, you can see it directly in the navigation bar.
Currently Cluster Orchestrator can be set up using two methods: a. Helm Based installation b. Script based installation via CCM UI and kubectl
Helm-based Installation
Prerequisites
- Helm 3.x installed: Ensure Helm is installed on your local machine.
- Kubernetes access: You should have access to the Kubernetes cluster where the orchestrator will be installed.
- Terraform setup: Run the Terraform script (provided below) to generate the necessary output variables.
Step 1: Run the Terraform Script
The Terraform script sets up the required infrastructure, including AWS IAM roles, subnets, security groups, and Harness service accounts, for the Harness CCM Cluster Orchestrator. Ensure you complete this step first before moving on to the Helm installation.
Terraform Template
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 5.86"
}
harness = {
source = "harness/harness"
version = "0.35.3"
}
}
required_version = ">= 1.2.0"
}
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-2"
}
variable "cluster" {
type = object({
name = string
oidc_arn = string
subnets = list(string)
security_groups = list(string)
ami = string
k8s_connector_id = string
existing_node_role = string
eks_pod_identity_enabled = bool
})
default = {
name = "cluster-xxx-xxx" // Replace with your EKS cluster Name
oidc_arn = "arn:aws:iam::xxx:oidc-provider/oidc.eks.xxx.amazonaws.com/id/xxxx" // Replace with your OIDC Provder ARN for the cluster
subnets = ["eksctl-xxx"] // Replace with the names of subnets used in your EKS cluster
security_groups = ["eks-cluster-sg-xxx"] // Replace with the names of security groups used in your EKS cluster
ami = "ami-i0xxxxxxxxx" // Replace with the id of AMI used in your EKS cluster
k8s_connector_id = "xxx" // Replace with the ID of harness ccm kubernetes connector for the cluster
existing_node_role = "RoleNameXXXX"
eks_pod_identity_enabled = false // Set to true if eks pod identity is enabled in the cluster
}
}
variable "harness" {
type = object({
endpoint = string
account_id = string
platform_api_key = string
cluster_orch_service_account_name = string
cluster_orch_namespace = string
})
default = {
endpoint = "https://app.harness.io/gateway"
account_id = "xxx" // Replace with your Harness Account ID
platform_api_key = "pat.xxx.xxx.xxx" // Replace with your Harness API key
cluster_orch_service_account_name = "ccm-clusterorchestrator" // Name of the service account used by cluster orchestrator
cluster_orch_namespace = "kube-system" // Namespace where the cluster orchestrator will be deployed
}
}
provider "harness" {
endpoint = var.harness.endpoint
account_id = var.harness.account_id
platform_api_key = var.harness.platform_api_key
}
data "aws_eks_cluster" "cluster" {
name = var.cluster.name
}
data "aws_iam_openid_connect_provider" "cluster_oidc" {
count = var.cluster.eks_pod_identity_enabled ? 0 : 1
arn = var.cluster.oidc_arn
}
data "aws_subnets" "cluster_subnets" {
filter {
name = "tag:Name"
values = var.cluster.subnets
}
}
data "aws_security_groups" "cluster_security_groups" {
filter {
name = "group-name"
values = var.cluster.security_groups
}
}
resource "aws_ec2_tag" "cluster_subnet_tag" {
for_each = toset(data.aws_subnets.cluster_subnets.ids)
resource_id = each.value
key = format("harness.io/%s", substr(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, 0, 40))
value = "owned"
}
resource "aws_ec2_tag" "cluster_security_group_tag" {
for_each = toset(data.aws_security_groups.cluster_security_groups.ids)
resource_id = each.value
key = format("harness.io/%s", substr(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, 0, 40))
value = "owned"
}
resource "aws_ec2_tag" "cluster_ami_tag" {
resource_id = var.cluster.ami
key = format("harness.io/%s", substr(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, 0, 40))
value = "owned"
}
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "assume_inline_policy" {
statement {
actions = ["sts:AssumeRole"]
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["ec2.amazonaws.com"]
}
effect = "Allow"
}
}
resource "aws_iam_role" "node_role" {
name = format("%s-%s-%s", "harness-ccm", substr(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, 0, 40), "node")
assume_role_policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.assume_inline_policy.json
description = format("%s %s %s", "Role to manage", data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, "EKS cluster used by Harness CCM")
managed_policy_arns = ["arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly", "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy", "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSClusterPolicy", "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSWorkerNodePolicy", "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore"]
}
resource "aws_eks_access_entry" "node_role_entry" {
cluster_name = var.cluster.name
principal_arn = aws_iam_role.node_role.arn
type = "EC2_LINUX"
}
resource "aws_iam_instance_profile" "instance_profile" {
name = format("%s-%s-%s", "harness-ccm", substr(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, 0, 40), "inst-prof")
role = aws_iam_role.node_role.name
}
resource "aws_iam_policy" "controller_role_policy" {
name_prefix = "ClusterOrchestratorControllerPolicy"
policy = jsonencode({
"Version" : "2012-10-17",
"Statement" : [
{
"Action" : [
"ec2:CreateLaunchTemplate",
"ec2:CreateFleet",
"ec2:RunInstances",
"ec2:CreateTags",
"iam:PassRole",
"ec2:TerminateInstances",
"ec2:DeleteLaunchTemplate",
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplates",
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups",
"ec2:DescribeSubnets",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceTypes",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceTypeOfferings",
"ec2:DescribeAvailabilityZones",
"ssm:GetParameter",
"pricing:GetProducts",
"ec2:DescribeSpotPriceHistory",
"ec2:DescribeImages"
],
"Resource" : "*",
"Effect" : "Allow"
}
]
})
}
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "oidc_controller_trust_policy" {
statement {
actions = ["sts:AssumeRole", "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity"]
principals {
type = "Federated"
identifiers = var.cluster.eks_pod_identity_enabled ? [] : [data.aws_iam_openid_connect_provider.cluster_oidc[0].arn]
}
effect = "Allow"
}
}
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "pod_identity_controller_trust_policy" {
statement {
sid = "AllowEksAuthToAssumeRoleForPodIdentity"
effect = "Allow"
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["pods.eks.amazonaws.com"]
}
actions = ["sts:AssumeRole", "sts:TagSession"]
}
}
resource "aws_iam_role" "controller_role" {
name = format("%s-%s-%s", "harness-ccm", substr(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, 0, 40), "controller")
assume_role_policy = var.cluster.eks_pod_identity_enabled ? data.aws_iam_policy_document.pod_identity_controller_trust_policy.json : data.aws_iam_policy_document.oidc_controller_trust_policy.json
description = format("%s %s %s", "Role to manage", data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, "EKS cluster controller used by Harness CCM")
managed_policy_arns = [aws_iam_policy.controller_role_policy.arn]
}
/*
uncomment to create eks addon for pod identity agent, if "eks-pod-identity-agent" is not present as addon in the cluster
resource "aws_eks_addon" "pod-identity-agent" {
count = var.cluster.eks_pod_identity_enabled ? 1 : 0
cluster_name = var.cluster.name
addon_name = "eks-pod-identity-agent"
}
*/
resource "aws_eks_pod_identity_association" "pod_identity_association" {
count = var.cluster.eks_pod_identity_enabled ? 1 : 0
cluster_name = data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name
namespace = var.harness.cluster_orch_namespace
service_account = var.harness.cluster_orch_service_account_name
role_arn = aws_iam_role.controller_role.arn
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "harness_describe_permissions" {
name = "HarnessDescribePermissions"
role = var.cluster.existing_node_role
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Action = [
"ec2:DescribeImages",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceTypeOfferings",
"ec2:DescribeInstanceTypes",
"ec2:DescribeAvailabilityZones"
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplates",
"ec2:CreateLaunchTemplate",
"ec2:CreateTags",
"pricing:GetProducts",
"ec2:DescribeSpotPriceHistory",
"ec2:CreateFleet",
"iam:PassRole",
"ec2:RunInstances",
"ec2:DeleteLaunchTemplate",
"ec2:TerminateInstances"
]
Effect = "Allow"
Resource = "*"
},
]
})
}
resource "harness_cluster_orchestrator" "cluster_orchestrator" {
name = substr(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, 0, 40)
cluster_endpoint = data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.endpoint
k8s_connector_id = var.cluster.k8s_connector_id
}
resource "harness_platform_service_account" "cluster_orch_service_account" {
identifier = replace(substr(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, 0, 40), "-", "_")
name = substr(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, 0, 40)
email = "email@service.harness.io"
description = "service account for cluster orchestrator"
account_id = var.harness.account_id
}
resource "harness_platform_role_assignments" "cluster_orch_role" {
resource_group_identifier = "_all_account_level_resources"
role_identifier = "_account_admin"
principal {
identifier = harness_platform_service_account.cluster_orch_service_account.id
type = "SERVICE_ACCOUNT"
}
}
resource "harness_platform_apikey" "api_key" {
identifier = replace(substr(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, 0, 40), "-", "_")
name = substr(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, 0, 40)
parent_id = harness_platform_service_account.cluster_orch_service_account.id
apikey_type = "SERVICE_ACCOUNT"
account_id = var.harness.account_id
}
resource "harness_platform_token" "api_token" {
identifier = "token"
name = replace(substr(data.aws_eks_cluster.cluster.name, 0, 40), "-", "_")
parent_id = harness_platform_service_account.cluster_orch_service_account.id
account_id = var.harness.account_id
apikey_type = "SERVICE_ACCOUNT"
apikey_id = harness_platform_apikey.api_key.id
}
output "harness_ccm_token" {
value = harness_platform_token.api_token.value
sensitive = true
}
output "eks_cluster_controller_role_arn" {
value = aws_iam_role.controller_role.arn
}
output "eks_cluster_default_instance_profile" {
value = aws_iam_instance_profile.instance_profile.name
}
output "eks_cluster_node_role_arn" {
value = aws_iam_role.node_role.arn
}
output "harness_cluster_orchestrator_id" {
value = harness_cluster_orchestrator.cluster_orchestrator.id
}
Terraform Outputs
Once the script is executed, it will generate several outputs required for the Helm installation:
harness_ccm_token: The Harness CCM token.eks_cluster_controller_role_arn: The ARN for the EKS cluster controller role.eks_cluster_default_instance_profile: The name of the default EC2 instance profile.eks_cluster_node_role_arn: The ARN for the node IAM role.harness_cluster_orchestrator_id: The Cluster Orchestrator ID.
Step 2: Add the Harness CCM Cluster Orchestrator Helm Repository
Add the Harness Helm chart repository:
helm repo add harness-ccm-cluster-orchestrator https://lightwing-downloads.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/cluster-orchestrator-helm-chart
Step 3: Update the Helm Repository
Ensure the Helm repository is up to date:
helm repo update harness-ccm-cluster-orchestrator
Step 4: Install/Upgrade the Cluster Orchestrator
After running the Terraform script and gathering the required output values, use the following Helm command to install or upgrade the Cluster Orchestrator.
Please note, after running the Terraform script, the API key will not be printed since it is sensitive data. To retrieve the value, you need to run terraform output harness_ccm_token
Replace the placeholders in the command with values from the Terraform outputs and your specific configuration:
helm install harness-ccm-cluster-orchestrator --namespace kube-system harness-ccm-cluster-orchestrator/harness-ccm-cluster-orchestrator \
--set harness.accountID="<harness_account_id>" \
--set harness.k8sConnectorID="<k8s_connector_id>" \
--set harness.ccm.secret.token="<harness_ccm_token>" \
--set eksCluster.name="<eks_cluster_name>" \
--set eksCluster.region="<eks_cluster_region>" \
--set eksCluster.controllerRoleARN="<eks_cluster_controller_role_arn>" \
--set eksCluster.endpoint="<eks_cluster_endpoint>" \
--set eksCluster.defaultInstanceProfile.name="<eks_cluster_default_instance_profile>" \
--set eksCluster.nodeRole.arn="<eks_cluster_node_role_arn>" \
--set clusterOrchestrator.id="<cluster_orchestrator_id>"
If your cluster does not have a OIDC provider arn, use this :-
eksctl utils associate-iam-oidc-provider --region <your_cluster_region> --cluster <your_cluster> --approve
Installation via kubectl
Step 1: Navigate to Cluster Orchestrator in the Cloud Costs Module
Click on Cluster Orchestrator from the navigation bar. Once you click on it, you will be taken to the home page, where you can see all the clusters associated with your account.
For each cluster, you can see the following information:
- Name of the cluster
- Region of the cluster
- Number of nodes associated with the cluster
- CPU
- Memory
- Potential spend of the cluster
- Savings realized
- Whether the Cluster Orchestrator is enabled for the particular cluster
On this page, you can also see the total cost of the clusters and the spot savings.
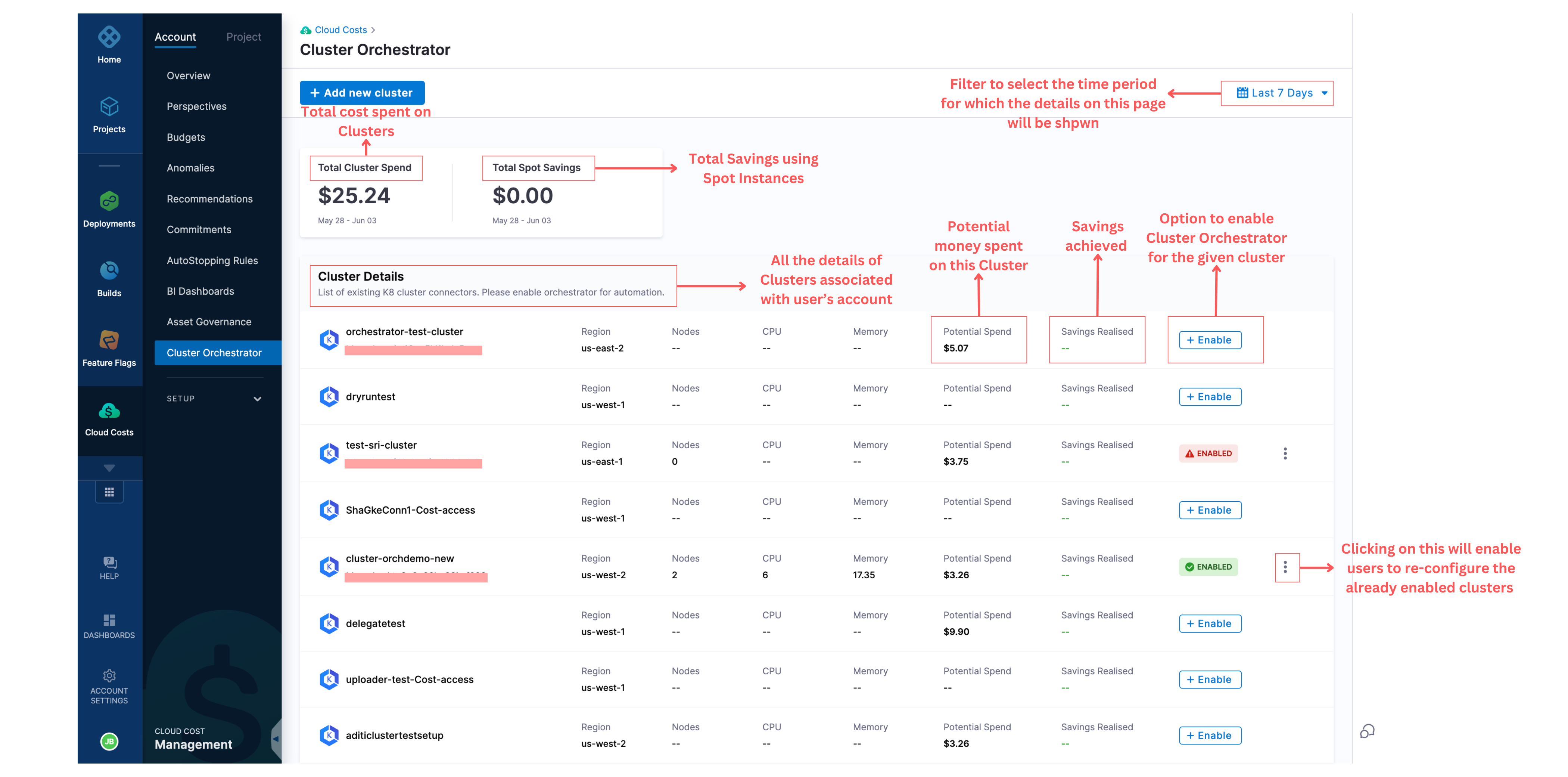
Step 2: Enable the Cluster Orchestrator for a Selected Cluster
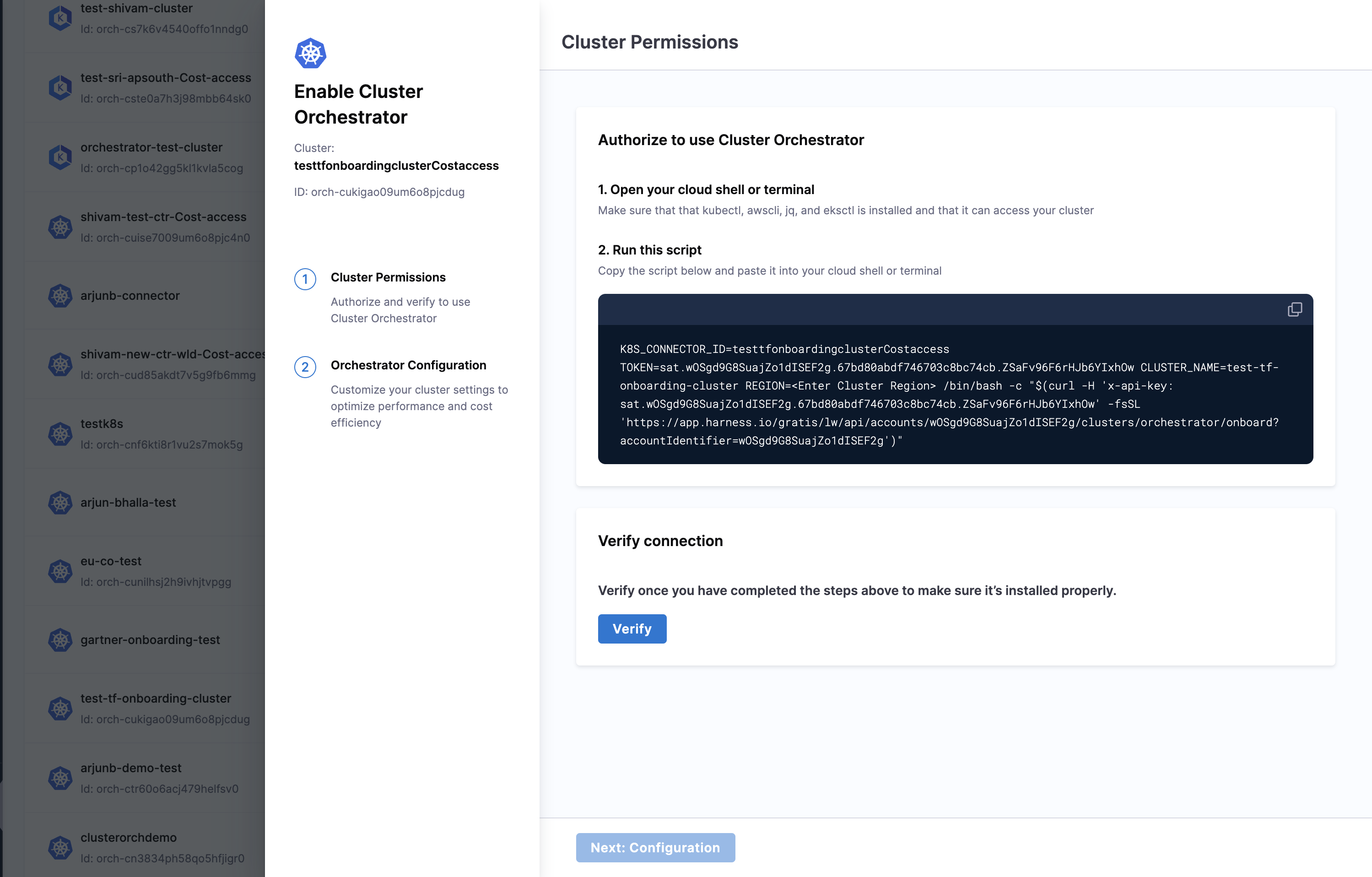
For a given cluster, click on the enable option, which will take you to the enablement screen. To enable the Cluster Orchestrator for the particular cluster, there are two steps to complete:
Step A: Cluster Permissions
You will be asked to run a shell script in your terminal and verify the connection. Upon successfully establishing the connection, click on the next step to configure.
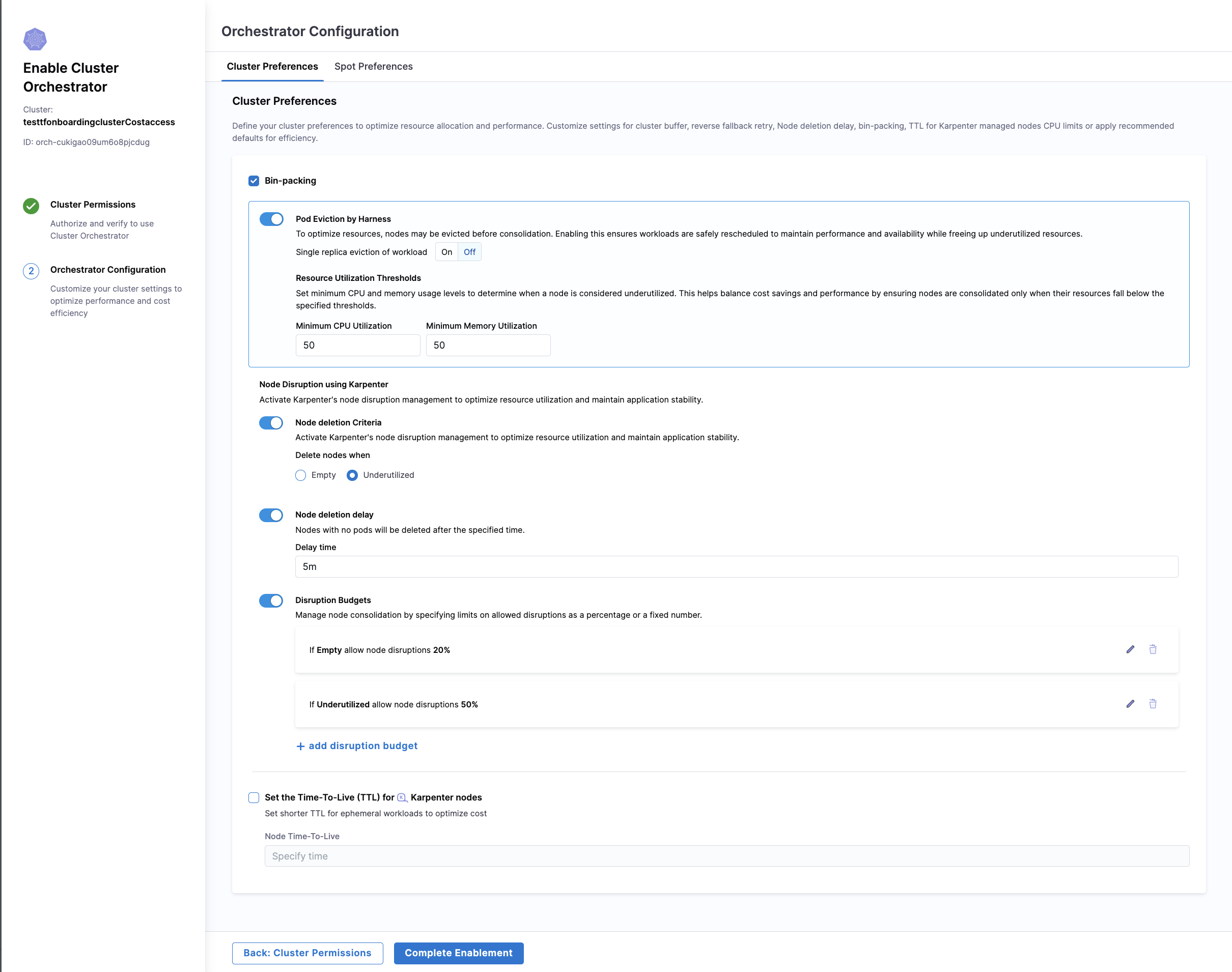
Step B: Orchestrator Configuration
Cluster Orchestrator allows you to choose Cluster Preferences and Spot Preferences.
Cluster Preferences:
-
Bin-Packing:
-
Pod Eviction by Harness: To optimize resources, nodes may be evicted before consolidation. Enabling pod eviction ensures workloads are safely rescheduled to maintain performance and availability while freeing up underutilized resources. Users can set single replica eviction of workload as On or Off.
-
Resource Utilization Thresholds: This is used to set minimum CPU and memory usage levels to determine when a node is considered underutilized. This helps balance cost savings and performance by ensuring nodes are consolidated only when their resources fall below the specified thresholds.
-
-
Node Disruption Using Karpenter: This option can be utilised to activate Karpenter's node disruption management to optimize resource utilization and maintain application stability. Cluster orchestrator provders three optional settings here:
- Node deletion criteria: The setting ensures that the nodes are deleted either when they are empty or under utilised as set by the user
- Node deletion delay: The setting ensures that the nodes with no pods are deleted after a specified time and the delay time can be set by the user
- Disruption Budgets: This feature allows users to define limits on the percentage of nodes that can be disrupted at any given time. This option comes with an added setting of selecting the reason and enabling or disabling budget scheduling
-
TTL for Karpenter Nodes: The Time-to-Live (TTL) setting for Karpenter nodes defines the maximum lifespan of a node before it is eligible for deletion, regardless of its resource utilization. By setting a TTL, users can ensure that idle or unnecessary nodes are automatically cleaned up after a specified time period, even if they are not underutilized or empty. This helps in avoiding resource sprawl, ensuring that unused nodes don’t linger indefinitely, and optimizing the overall cost and resource usage within the cluster.
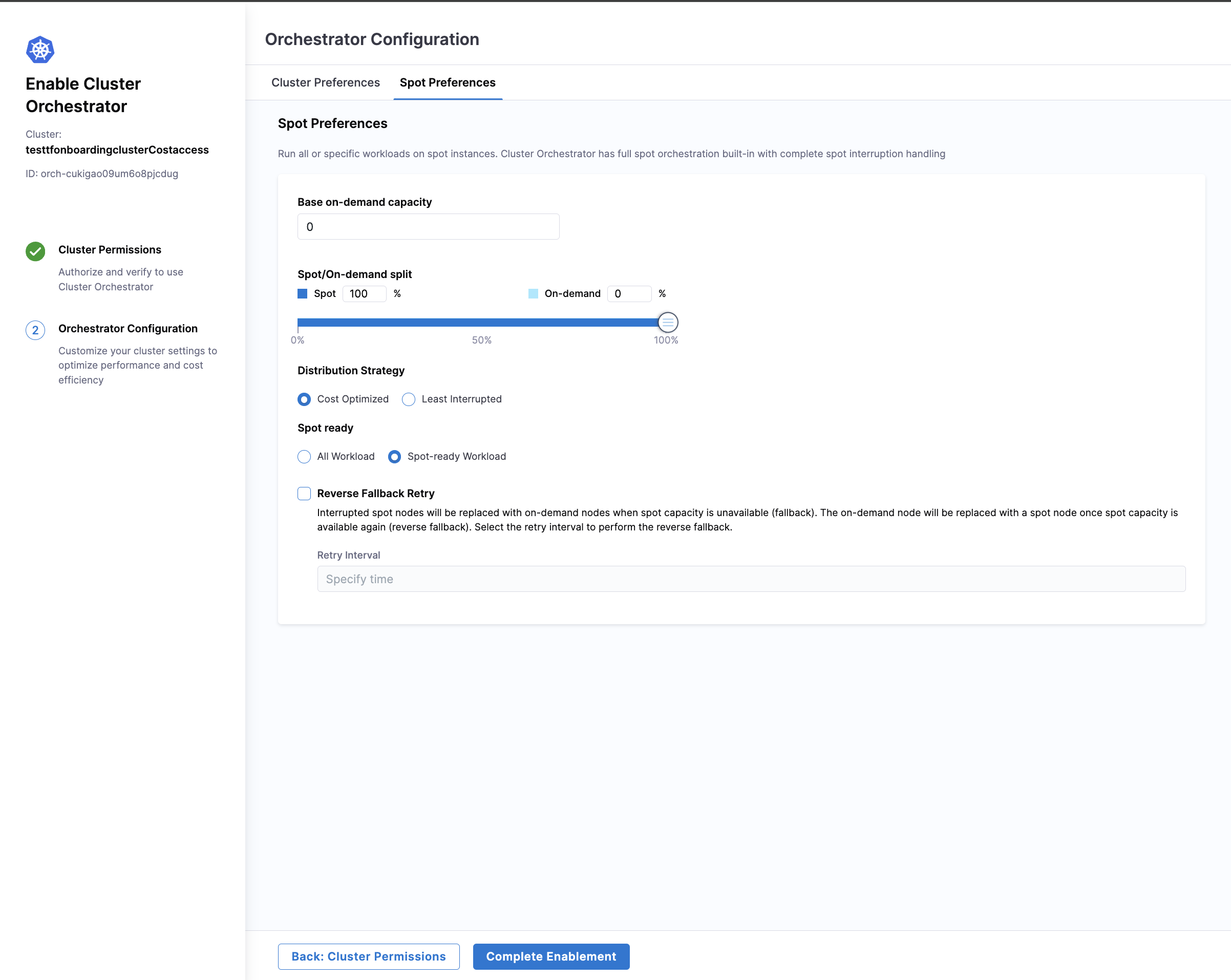
Spot Preferences:
Cluster Orchestrator allows users to set Base On-Demand Capacity, which can be further split into percentages to determine how much should be used by Spot and On-Demand instances. You can also choose the distribution strategy between Least-Interrupted or Cost-optimized and can define spot-ready for all workloads or spot-ready workloads.
Users can also enable reverse fallback retry. When spot nodes are interrupted, they are automatically replaced with on-demand nodes to maintain application stability. Once spot capacity becomes available again, the system will perform a reverse fallback, replacing the on-demand node with a spot node. Users can select the retry interval to define how often the system checks for spot capacity and performs the reverse fallback.
Once all the details are filled in, click on the "Complete Enablement" button to enable Cluster Orchestrator for the cluster.
After the setup is complete, Cluster Orchestrator supports three screens to show information about your cluster:
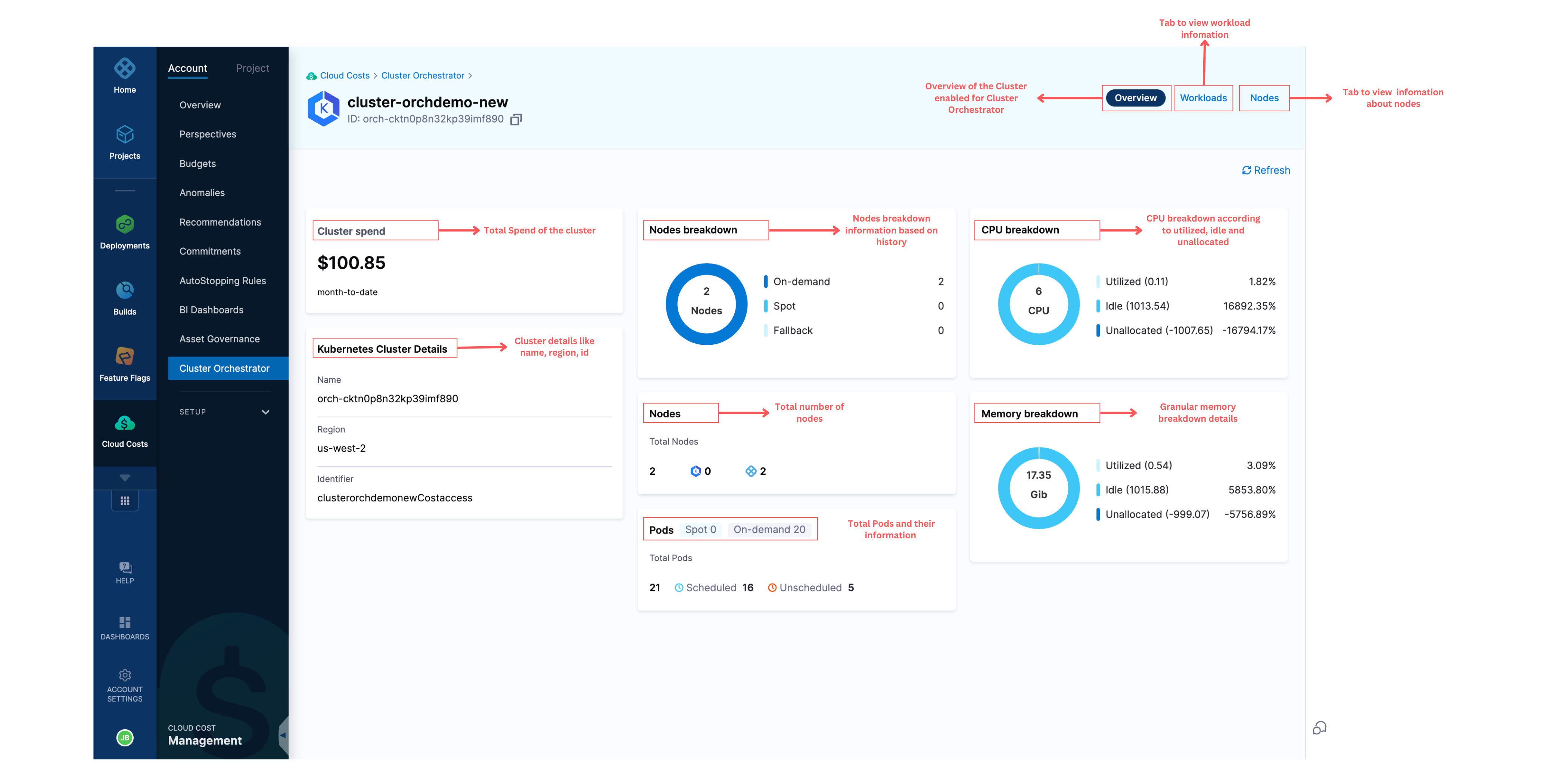
Overview Page for Cluster Orchestrator Enabled Clusters
The overview page shows all the information about:
- Cluster Spend
- Cluster Details
- Nodes Breakdown
- Nodes
- Pods
- CPU Breakdown
- Memory Breakdown
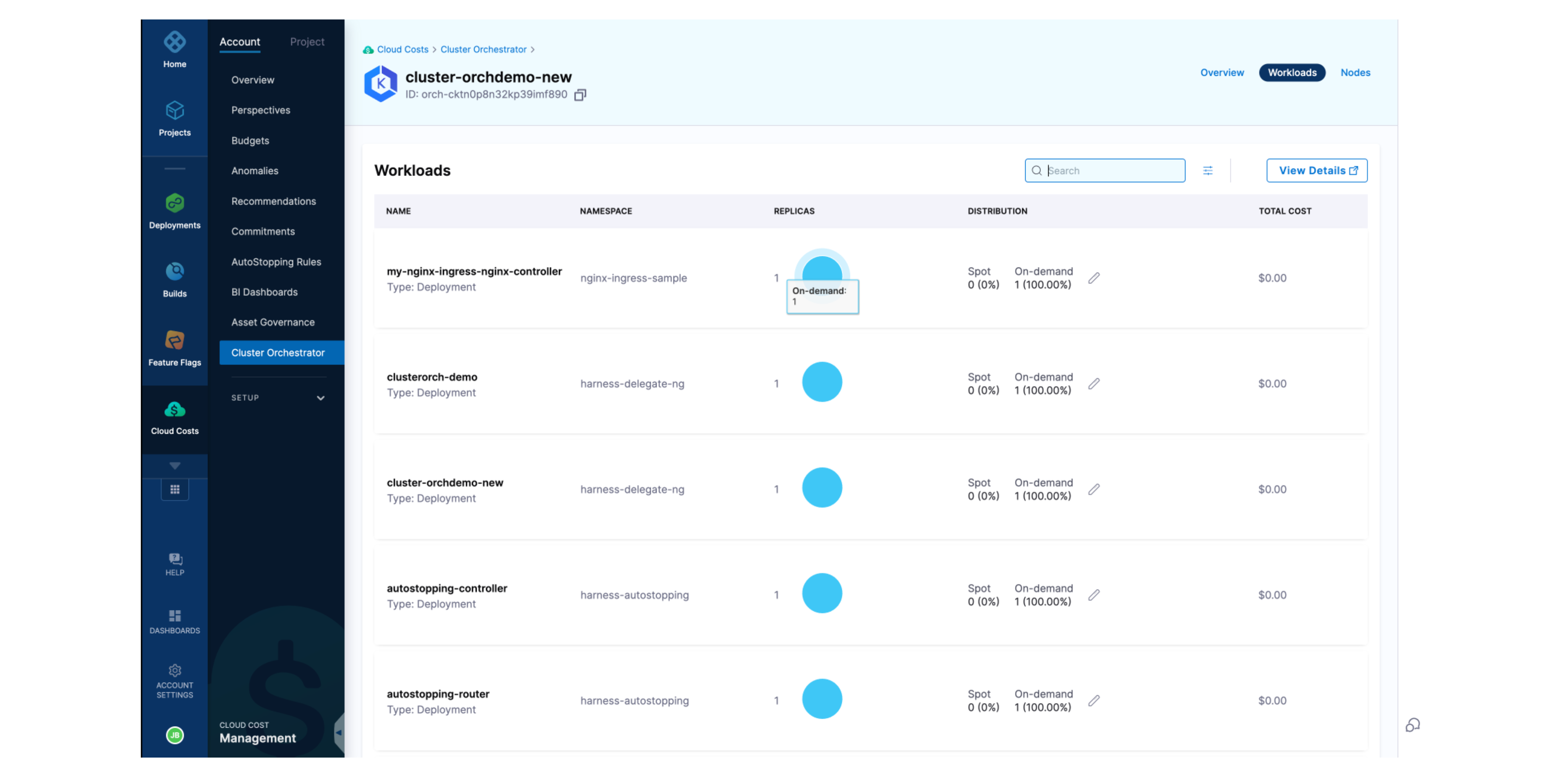
Overview of Workloads in the Cluster
This page contains all the information about the workloads associated with the cluster including their:
- Namespace
- Replicas
- Distribution of Replicas
- Total Cost of each workload.
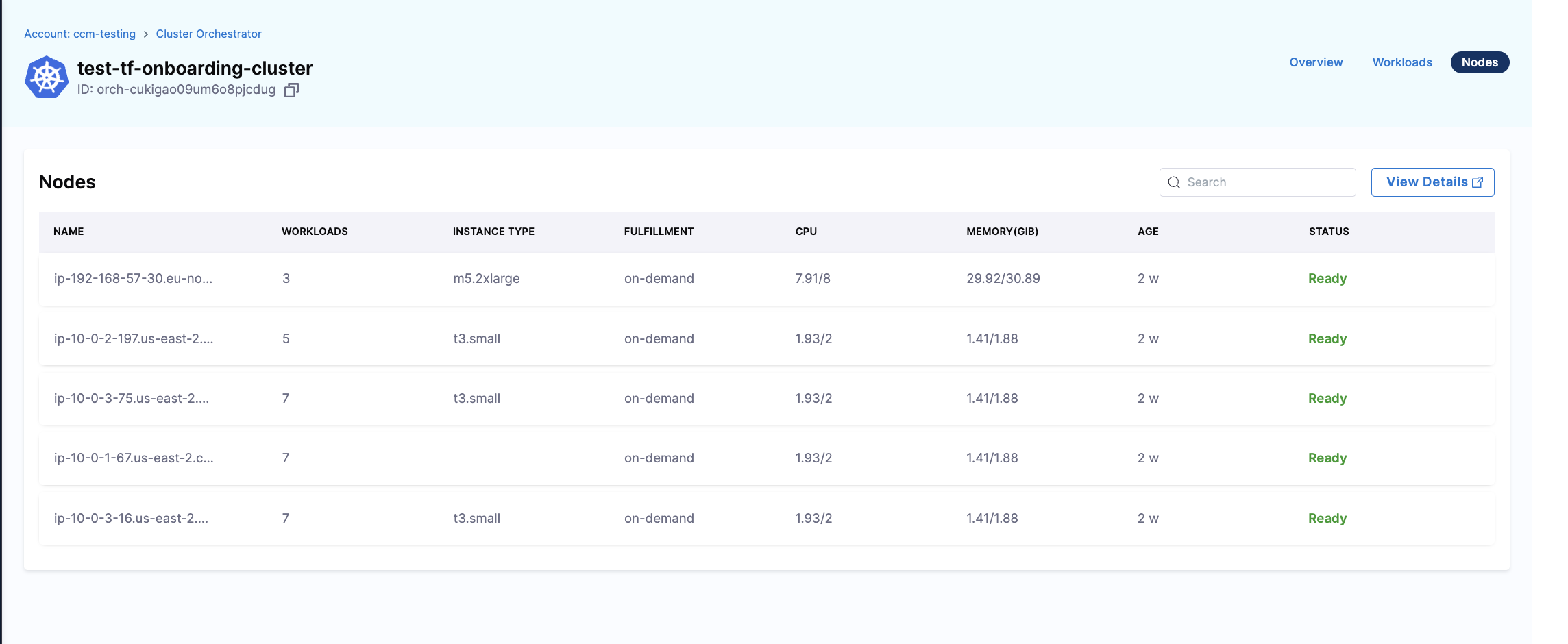
Overview of Nodes in the Cluster
This page contains all the information about the nodes associated with the cluster, including:
- the Number of Workloads
- Instance Types
- Fulfillment
- CPU
- Memory
- Age
- Status
Additionally, you can see the details of all nodes.