Use Run Tests step for Java, Kotlin, or Scala
This page contains instructions for using Test Intelligence (v1) with the Run Tests step.
While Run Tests step remains backwards compatible, Harness recommends using the newer Test step (Test Intelligence v2) for simplified user experience.
Enable TI for Java, Kotlin, or Scala
Test Intelligence requires that the code is cloned into the default workspace directory, /harness/. If the code is placed elsewhere, Test Intelligence will not function correctly.
You can enable TI for Java, Kotlin, or Scala in three steps:
- Add a Run Tests step. For Java consider using the new Test step instead.
- Trigger test selection.
- (Optional) Add test splitting.
Add the Run Tests step
Add the Run Tests step to the Build stage in a CI pipeline.
You must select Run only selected tests (runOnlySelectedTests: true) to enable Test Intelligence. For information about each setting, go to Run Tests step settings.
- step:
type: RunTests
name: Run Tests
identifier: Run_Tests
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage ## Specify if required by your build infrastructure.
image: maven:3.8-jdk-11 ## Specify if required by your build infrastructure.
language: Java ## Specify Java, Kotlin, or Scala.
buildTool: Maven ## Specify your build tool.
args: test
packages: io.harness.
runOnlySelectedTests: true ## Must be 'true' to enable TI.
postCommand: mvn package -DskipTests
reports: ## Reports must be in JUnit XML format.
type: JUnit
spec:
paths:
- "target/reports/*.xml"
For additional YAML examples, go to Pipeline YAML examples
Additional configuration needed when using Kotlin with Gradle
If you are using Test Intelligence for Kotlin and building using Gradle, add the below section to the build.gradle.kts file under the 'allprojects' section.
tasks.withType<Test> {
val harnessJavaAgent = System.getProperty("HARNESS_JAVA_AGENT")
if (harnessJavaAgent != null) {
jvmArgs(harnessJavaAgent)
}
}
gradle.projectsEvaluated {
tasks.withType<Test> {
filter {
isFailOnNoMatchingTests = false
}
}
}
Trigger test selection
After adding the Run Tests step, trigger test selection. You need to run your pipeline twice to trigger test selection.
Trigger test selection with a webhook trigger (Recommended)
Trigger test selection with a manual build
The first time you run a pipeline after adding the Run Test step, Harness creates a baseline for test selection in future builds. Test selection isn't applied to this run because Harness has no baseline against which to compare changes and select tests. You'll start seeing test selection and time savings on the second run after adding the Run Tests step.
Add test splitting
Once you start saving time with test selection, you can further optimize test times by enabling parallelism (test splitting) for TI.
You can also configure TI to ignore tests or files.
Pipeline YAML examples
- Harness Cloud
- Self-managed
This example shows a pipeline that uses Harness Cloud build infrastructure and runs tests on Java with Maven and Test Intelligence. By changing the language value, you can use this pipeline for Kotlin or Scala.
pipeline:
name: Test Intelligence Demo
identifier: testintelligencedemo
projectIdentifier: default
orgIdentifier: default
properties:
ci:
codebase:
build: <+input>
connectorRef: YOUR_CODEBASE_CONNECTOR_ID
stages:
- stage:
type: CI
identifier: Build_and_Test
name: Build and Test
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: RunTests
name: Run Tests
identifier: Run_Tests
spec:
language: Java ## Specify Java, Kotlin, or Scala.
buildTool: Maven ## For Java or Kotlin, specify Bazel, Maven, or Gradle. For Scala, specify Bazel, Maven, Gradle, or Sbt.
args: test
packages: io.harness.
runOnlySelectedTests: true ## Must be 'true' to enable TI.
postCommand: mvn package -DskipTests
reports: ## Reports must be in JUnit XML format.
type: JUnit
spec:
paths:
- "target/reports/*.xml"
platform:
arch: Amd64
os: Linux
runtime:
spec: {}
type: Cloud
This example shows a pipeline that uses a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure and runs tests on Java with Maven and Test Intelligence. By changing the language value, you can use this pipeline for Kotlin or Scala.
pipeline:
name: Test Intelligence Demo
identifier: testintelligencedemo
projectIdentifier: default
orgIdentifier: default
properties:
ci:
codebase:
build: <+input>
connectorRef: YOUR_CODEBASE_CONNECTOR_ID
stages:
- stage:
type: CI
identifier: Build_and_Test
name: Build and Test
spec:
cloneCodebase: true
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: RunTests
name: Run Tests
identifier: Run_Tests
spec:
connectorRef: account.harnessImage ## Specify if required by your build infrastructure.
image: maven:3.8-jdk-11 ## Specify if required by your build infrastructure.
language: Java ## Specify Java, Kotlin, or Scala.
buildTool: Maven ## For Java or Kotlin, specify Bazel, Maven, or Gradle. For Scala, specify Bazel, Maven, Gradle, or Sbt.
args: test
packages: io.harness.
runOnlySelectedTests: true ## Must be 'true' to enable TI.
postCommand: mvn package -DskipTests
reports: ## Reports must be in JUnit XML format.
type: JUnit
spec:
paths:
- "target/reports/*.xml"
infrastructure:
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_KUBERNETES_CLUSTER_CONNECTOR_ID
namespace: YOUR_KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE
automountServiceAccountToken: true
nodeSelector: {}
os: Linux
Run Tests step settings
The following information explains how to configure most settings for the Run Tests step. You might not need all settings for all scenarios; some settings are optional, and some settings are only available for specific languages, build tools, or build infrastructures.
Container Registry and Image
The build environment must have the necessary binaries for the Run Tests step to execute your test commands. Depending on the stage's build infrastructure, Run Tests steps can use binaries that exist in the build environment, or use Container Registry and Image to pull an image, such as a public or private Docker image, that contains the required binaries. You can also install tools at runtime in Pre-Command, provided the build machine or image can execute the necessary commands, such as curl commands to download files.
When are Container Registry and Image required?
What are the expected values for Container Registry and Image?
Bazel container images
Language
Select the source code language to build: Java, Kotlin, or Scala.
Build Tool
Select the build automation tool: Bazel, Maven, Gradle, or Sbt (Scala only).
Bazel container images
Java Maven argLine setup
Java Gradle compatibility
Build Arguments
This setting is required for Java, Kotlin, and Scala.
Enter commands to use as input or runtime arguments for the build tool. You don't need to repeat the build tool, such as maven, this is declared in Build Tool.
This can be as simple as test or you can include additional flags, such as: test -Dmaven.test.failure.ignore=true -DfailIfNoTests=false.
Test Report Paths
This setting is required for the Run Tests step to publish test results.
Specify one or more paths to files that store test results in JUnit XML format. Glob is supported.
You can add multiple paths. If you specify multiple paths, make sure the files contain unique tests to avoid duplicates.
Test Splitting (parallelism)
Used to enable test splitting (parallelism) for TI.
Pre-Command, Post-Command, and Shell
- Pre-Command: You can enter commands for setting up the environment before running the tests, such as
mvn clean package dependency:copy-dependencies - Post-Command: You can enter commands used for cleaning up the environment after running the tests, such as
mvn package -DskipTests. - Shell: If you supplied a script in Pre-command or Post-command, select the corresponding shell script type.
Packages
Leave blank or provide a comma-separated list of source code package prefixes, such as com.company., io.company.migrations. If you do not provide a list, Harness auto-detects the packages.
Run Only Selected Tests
This option must be selected (true) to enable Test Intelligence.
If this option is not selected (false), TI is disabled and all tests run on every build.
Test Annotations
You can provide a comma-separated list of test annotations used in unit testing. Any method with a specified annotation is treated as a test method.
This setting is optional. If not specified, the defaults are: org.junit.Test, org.junit.jupiter.api.Test, org.testing.annotations.Test.
This setting is located under Additional Configuration in the Visual editor, or you can configure it in YAML as:
testAnnotations: annotation1, annotation2, annotation3
Environment Variables
You can inject environment variables into the step container and use them in the step's commands. You must input a Name and Value for each variable.
You can reference environment variables in the Build Arguments, Pre-Command, or Post-Command scripts by name, such as $var_name.
Variable values can be fixed values, runtime inputs, or expressions. For example, if the value type is expression, you can input a value that references the value of some other setting in the stage or pipeline.
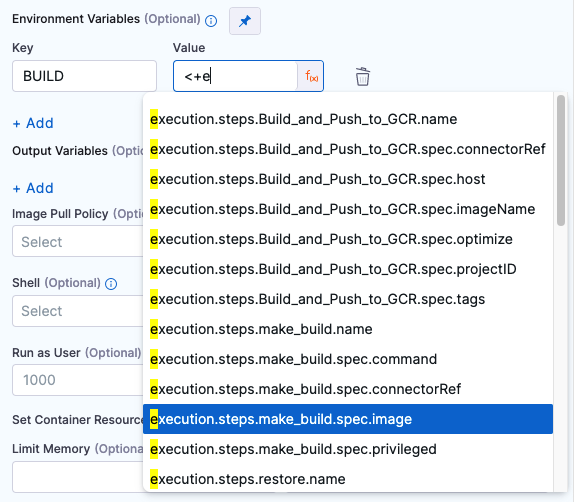
Stage variables are inherently available to steps as environment variables.
Additional container settings
Settings specific to containers are not applicable in a stages that use VM or Harness Cloud build infrastructure.
Image Pull Policy
If you specified a Container Registry and Image, you can specify an image pull policy:
- Always: The kubelet queries the container image registry to resolve the name to an image digest every time the kubelet launches a container. If the kubelet encounters an exact digest cached locally, it uses its cached image; otherwise, the kubelet downloads (pulls) the image with the resolved digest, and uses that image to launch the container.
- If Not Present: The image is pulled only if it isn't already present locally.
- Never: The image is not pulled.
Run as User
If you specified a Container Registry and Image, you can specify the user ID to use for running processes in containerized steps.
For a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure, the step uses this user ID to run all processes in the pod. For more information, go to Set the security context for a pod.
Privileged
For container-based build infrastructures, you can enable this option to run the container with escalated privileges. This is equivalent to running a container with the Docker --privileged flag.
Set Container Resources
These settings specify the maximum resources used by the container at runtime. These setting are only available for container-based build infrastructures, such as a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure.
- Limit Memory: The maximum memory that the container can use. You can express memory as a plain integer or as a fixed-point number using the suffixes
GorM. You can also use the power-of-two equivalentsGiandMi. The default is500Mi. - Limit CPU: The maximum number of cores that the container can use. CPU limits are measured in CPU units. Fractional requests are allowed. For example, you can specify one hundred millicpu as
0.1or100m. The default is400m. For more information go to Resource units in Kubernetes.
Timeout
You can set the step's timeout limit. Once the timeout is reached, the step fails and pipeline execution proceeds according to any Step Failure Strategy settings or Step Skip Condition settings.
Troubleshoot Test Intelligence
Go to the CI Knowledge Base for questions and issues related to Test Intelligence, including:
- Does Test Intelligence split tests? Can I use parallelism with Test Intelligence?
- Test Intelligence call graph is empty.
- If the Run Tests step fails, does the Post-Command script run?
- Test Intelligence fails due to Bazel not installed, but the container image has Bazel.
- Test Intelligence fails with error 'Unable to get changed files list'.